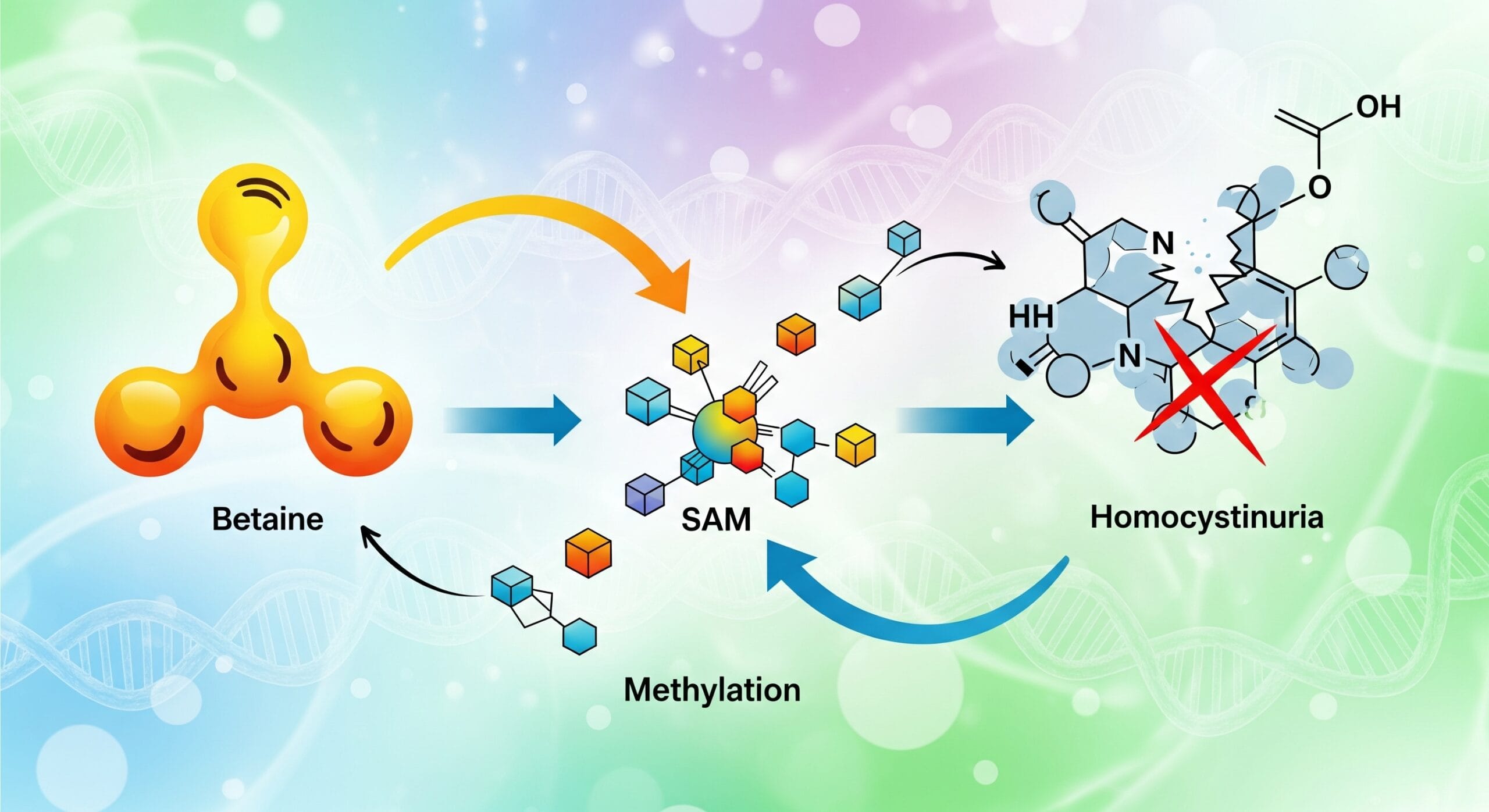
Integrating genetic, blood, and organic acid testing into patient care can provide profound insights into an individual’s health. However, to make the most of these tests, it’s essential to follow a strategic approach. Here’s a breakdown of the critical first steps for practitioners to ensure that they’re identifying, prioritising, and addressing the key health insights for each patient.
1. Identify Key Genetic Susceptibilities (or “Potholes”)
Genetic testing is like looking at a patient’s health roadmap. Certain genetic variations, or SNPs, act as “potholes” that can influence health outcomes, making it important to understand where these genetic vulnerabilities lie. When first assessing genetic data, focus on SNPs that have immediate clinical relevance—those that directly impact areas like methylation, detoxification, neurotransmitter function, or inflammation.